Explore the advantages and potential drawbacks of cloud computing for businesses. Learn how harnessing the power of the cloud can enhance productivity, scalability, and cost-efficiency, while also understanding the associated risks and considerations for data security and vendor dependencies.
Embracing the Cloud Revolution
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, businesses are continually seeking innovative solutions to stay ahead of the curve. One such groundbreaking technology that has taken the world by storm is cloud computing. This powerful tool has revolutionized the way organizations store, manage, and access their data and applications.
If you’re a business owner, IT professional, or decision-maker at the beginning of your career, understanding the benefits and risks of cloud computing is crucial to your success. This comprehensive guide aims to provide an in-depth exploration of cloud computing, its advantages and potential drawbacks, and best practices to help you make informed decisions.
Cloud Computing Demystified
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing resources, including software, storage, and processing power, over the Internet. Instead of purchasing and managing physical hardware and infrastructure, businesses can access these resources on-demand from cloud service providers. This enables organizations to focus on their core competencies while leveraging the latest technology advancements.
Types of Cloud Services: The Big Three
There are three primary types of cloud services, each catering to different needs:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): IaaS provides virtualized computing resources such as virtual machines, storage, and networking over the Internet. Examples include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform, and Microsoft Azure.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): PaaS offers a platform for developers to build, test, and deploy applications without worrying about underlying infrastructure management. This service includes tools, middleware, and databases required for app development. Examples of PaaS providers include Heroku, Google App Engine, and Microsoft Azure App Service.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): SaaS delivers ready-to-use software applications over the Internet, typically through a subscription model. Users can access these applications from any device with an internet connection. Popular SaaS providers include Salesforce, Microsoft Office 365, and Google Workspace.
Major Cloud Service Providers: The Powerhouses
Some of the most popular cloud service providers dominating the market are:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
- Microsoft Azure
These providers offer various cloud services, ranging from IaaS to SaaS, catering to businesses of all sizes.

Benefits of Cloud Computing for Businesses
Cloud computing has revolutionized the way businesses operate in the digital age. By allowing companies to store, manage, and process their data and applications on remote servers accessed via the Internet, cloud computing has become a game-changer for businesses of all sizes. In this section, we will explore the benefits of cloud computing for businesses.
- Cost Savings: One of the biggest advantages of cloud computing is its cost-effectiveness. By leveraging cloud services, businesses can save on hardware and infrastructure costs and the costs associated with maintaining and managing their own data centers. Cloud providers offer a pay-as-you-go model, which allows businesses to scale their usage up or down based on their needs, making it a more cost-efficient option for small and medium-sized businesses.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Cloud computing provides businesses with the ability to quickly and easily scale their resources up or down as needed. This means that businesses can easily adapt to changing business needs and handle sudden spikes in traffic without incurring additional costs. Additionally, cloud services offer a variety of deployment models, such as public, private, and hybrid clouds, which can be tailored to meet specific business needs.
- Increased Collaboration and Productivity: Cloud computing promotes collaboration and productivity by allowing employees to access files and applications from anywhere, on any device, at any time. This leads to increased efficiency, better communication, and faster decision-making.
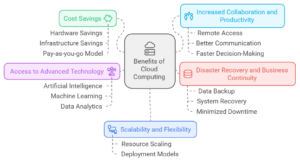
- Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity: Cloud computing offers businesses a reliable disaster recovery and business continuity solution. By backing up data and applications to remote servers, businesses can quickly and easily recover their systems in the event of a disaster. This minimizes downtime and ensures business continuity.
- Access to Advanced Technology: Cloud providers offer businesses access to advanced technology, such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and data analytics, that might otherwise be out of reach. This allows businesses to stay competitive and gain a competitive edge in their industry.
Risks of Cloud Computing for Businesses
While cloud computing offers numerous benefits to businesses, there are also inherent risks associated with storing and processing sensitive data on remote servers accessed via the Internet. In this section, we will explore the risks of cloud computing for businesses.
As a beginner in your career, it is important to understand the potential risks of cloud computing and to develop the skills and knowledge necessary to mitigate these risks and ensure the success of your business.
- Security Risks: One of the main concerns businesses have about cloud computing is security. Storing data and applications in remote servers accessible over the internet increases the risk of cyber-attacks and data breaches. Businesses must ensure that they have proper security measures in place, such as data encryption and access controls, to mitigate these risks.
- Compliance Risks: Many industries, such as healthcare and finance, have strict regulations and compliance requirements that must be followed. Storing data and applications in the cloud may pose compliance risks if cloud providers do not meet the necessary standards. Businesses must ensure that their cloud provider is compliant with all relevant regulations and standards.
- Dependence on Internet Connectivity: Cloud computing relies heavily on Internet connectivity. If the internet goes down, businesses may lose access to their data and applications, which could result in significant downtime and lost revenue.
- Lack of Control and Customization: Cloud providers may limit the level of control and customization businesses have over their systems. This can be problematic for businesses that require a high degree of control over their infrastructure or need to customize their systems to meet their specific needs.
- Service Outages and Downtime: Cloud providers are not immune to service outages and downtime. In the event of a service outage, businesses may lose access to their data and applications, which could result in significant downtime and lost revenue.

Strategies for Mitigating Cloud Computing Risks
To take advantage of the benefits of cloud computing while minimizing the associated risks, businesses must implement proper risk management strategies.
- Proper Data Protection and Encryption: Businesses must ensure that their data is properly protected and encrypted, both in transit and at rest. This includes using strong encryption algorithms and access controls to limit who has access to sensitive data.
- Compliance with Regulations and Standards: Businesses must ensure that their cloud provider is compliant with all relevant regulations and standards. This includes conducting due diligence and regularly monitoring their provider’s compliance status.
- Regular Backups and Disaster Recovery Planning: Businesses should have a disaster recovery plan in place that includes regular backups of their data and applications. This ensures that they can quickly recover from a disaster or service outage.
- Vendor Management and Due Diligence: Businesses should conduct due diligence when selecting a cloud provider and regularly monitor their provider’s performance and security practices. This includes reviewing their security policies, certifications, and compliance status.
- Continuous Monitoring and Auditing: Businesses should regularly monitor their cloud environment for potential security threats and vulnerabilities. This includes performing regular audits and vulnerability assessments to identify and address any security issues.
Conclusion
The benefits of cloud computing for businesses are undeniable, from cost savings and scalability to improved collaboration and enhanced security. However, it’s crucial to understand and manage potential risks to fully leverage this powerful technology.
As a beginner in your career, it is important to understand the benefits and risks of cloud computing and to develop the skills and knowledge necessary to implement proper risk management strategies to ensure the success of your business.
By embracing cloud computing and implementing best practices to mitigate risks, budding entrepreneurs and developers can unlock new opportunities and drive their businesses forward in the digital age.
Ready to innovate and transform your business? Say hello to CodeBeavers!
If you are looking for ways to bring your product or app ideas to life? We’ve got your back. CodeBeavers has the tools and engineers you need to make your projects come alive. With CodeBeavers, you’ll be able to build faster than ever, deploy code with ease, and scale like never before. Send us your requirements now, and let’s start winning together.




