Discover the key differences between cloud databases and on-premises databases and gain insights to determine the best fit for your business. Explore the benefits and challenges of each option, including scalability, cost, security, and management. Whether you're a small startup or a large enterprise, this article will help you make an informed decision about choosing the right database solution that aligns with your organization's needs and goals.
In today’s rapidly shifting digital landscape, efficiently managing data is of paramount importance for businesses of all sizes. Companies across industries need to choose the right database infrastructure to facilitate their data storage, management, and analytics needs.
This blog post will delve into the debate between cloud databases and on-premises databases to help developers and business owners make informed decisions. We’ll unpack the pros, cons, security considerations, implementation tips, and how a hybrid approach might work best for some companies.
Overview of Cloud Databases vs. On-Premises Databases
To help you appreciate the differences between cloud and on-premises databases, we will first define each option and discuss their relevance to your business.
Cloud Databases: Cloud databases are hosted, managed, and maintained by a third-party cloud service provider like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud Platform (GCP). These databases are delivered over the Internet, giving you the ability to access, store, manage, and analyze data from anywhere with an Internet connection.
On-Premises Databases: On-premises databases reside within your organization’s physical premises, typically on the company’s own servers. This means you’re responsible for providing the infrastructure, hardware, and software required to manage the database. On-premises databases are perceived to be more secure than the cloud since you’re in full control of your data.
Understanding the differences between these two options is essential for determining which is the best fit for your organization’s needs and operational environment.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Cloud Databases
- Scalability: Cloud databases can easily scale resources like storage and computing power, allowing you to handle growing data requirements without the need to invest in additional hardware.
- Accessibility: Your data and applications are available from anywhere, at any time, as long as you have an internet connection.
- Cost: Cloud databases typically operate on a pay-as-you-go model, which means you only pay for the resources you consume.
- Automation: Many cloud database providers offer automated data management tasks like backups, disaster recovery, and maintenance.
- Security Concerns: Storing sensitive data outside the control of your own organization could expose vulnerabilities, especially if the cloud provider’s security measures aren’t up to your organization’s standards.
- Latency: Data transfer speeds between your organization and the cloud database might not always be ideal, affecting performance and user experience.
- Vendor Lock-In: Switching cloud providers can be a costly and time-consuming process, forcing you to stick with a particular provider.
Advantages and Disadvantages of On-Premises Databases
- Data Control: You have complete control over physical access to your data, making it easier to enforce strict data security protocols.
- Customization: On-premises databases allow for greater flexibility in tailoring the database infrastructure to your organization’s specific needs.
- Data Sovereignty: On-premises databases enable you to comply with local data protection regulations more easily.
- High Initial and Ongoing Costs: You need to purchase, maintain, and upgrade hardware, software, and infrastructure to accommodate growing data needs.
- Limited Flexibility: Scaling resources on-premises can involve time-consuming and expensive hardware procurement, setup, and configuration.
- Maintenance Challenges: On-premises databases require dedicated IT staff for maintenance, troubleshooting, and performance optimization.
- Security Vulnerabilities: If not properly managed, on-premises systems can be vulnerable to malicious attacks. It is also challenging to ensure security compliance with relevant laws and regulations.
- Data Mobility: On-premises databases cannot be easily migrated or shared across multiple locations or systems, making it difficult to access data from remote locations or integrate with other applications.


Making an Informed Decision About Your Database Needs
The choice between cloud and on-premises databases often boils down to an organization’s specific requirements, which include factors like scalability, security, data sovereignty, and budget. Understanding your business objectives, the type and size of data to be stored, and any legal or compliance requirements can help guide you toward the right decision.
Cloud databases are services hosted and maintained by third-party providers, offering elastic scaling and pay-as-you-go pricing. On the other hand, on-premises databases are managed within a company’s own infrastructure with dedicated hardware, software, and personnel.
Oracle, for instance, switched its entire business model to the cloud, resulting in a significant revenue increase, while organizations like Barclays have opted for on-premises solutions due to strict industry regulations.
Cost Considerations and Security for Either Option
A crucial factor in the cloud vs. on-premises debate is cost. Cloud databases offer more predictable and flexible pricing models, where you only pay for the resources you consume. Cloud databases offer pay-as-you-go pricing, which means that organizations only pay for what they use.
This makes cloud databases a cost-effective option for businesses that want to avoid significant upfront costs. On the other hand, On-premises databases require significant investment in hardware, software, and personnel. However, in the long term, the ongoing expenses may outweigh the upfront costs of setting up an on-premises solution.
Security is another important aspect, as data breaches can lead to not only financial but also reputational damage. Both options pose security risks, but cloud databases benefit from the provider’s expertise in securing and patching their infrastructure. In contrast, on-premises solutions require in-house security resources, which might be budget-constraining for some companies.
While cloud databases are generally secure, some organizations may have specific security requirements that make an on-premises database a better option. With an on-premises database, companies have greater control over security protocols and can configure them to their specific needs.
For example, Shopify has embraced a cloud-based infrastructure to scale its e-commerce platform while maintaining robust security, whereas Apple keeps its data strictly on-premises to maintain control and assurance of data protection.

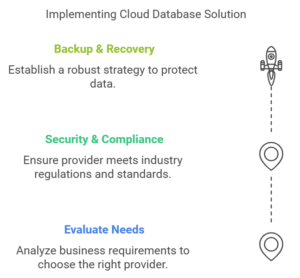
Tips for Implementing a Cloud Database Solution
Cloud databases have become increasingly popular due to their scalability, flexibility, and potential cost savings. If you’re considering a cloud database solution for your business, consider the following tips to ensure you make the most out of it:
- Evaluate Your Needs: Analyze your business or application requirements and choose a cloud service provider that offers the specific features you need, such as processing power, storage capacity, and supported languages and frameworks.
- Security & Compliance: Research the provider’s security measures and certifications, ensuring they meet your industry’s regulations and standards.
- Backup & Recovery: Ensure you have a solid backup and recovery strategy in place to protect your data from potential disasters or loss.
For instance, Netflix migrated its services to the cloud, and it now leverages AWS’s vast resources and data centers to process millions of user requests and serve thousands of hours of content every day.
Getting the Most Out of Your On-Premises Database Solution
On-premises databases grant businesses full control over their IT infrastructure while ensuring security and regulatory compliance. However, the upfront costs and required maintenance can be a drawback for some. To maximize the value of your on-premises database solution, consider the following guidance:
- Optimize Performance: Regularly monitor, analyze, and optimize your database’s performance, removing any bottlenecks and identifying opportunities for improvement.
- Invest in Regular Maintenance: Keep your hardware and software up-to-date, and schedule regular maintenance to ensure peak performance and prevent potential issues.
- Train Your IT Staff: Invest in training for your IT team, ensuring they have the necessary skills to maintain and manage your on-premises database solution effectively.
Take Bank of America, for example, which adopted a private cloud infrastructure for better control over its vast operations instead of moving to external cloud services.
The Benefits of a Hybrid Approach
In recent years, a third option has emerged that combines the best of both worlds: hybrid database solutions. This approach allows businesses to leverage the advantages of both on-premises and cloud databases, enabling developers and business owners to choose the right mix according to their specific needs. Below are some of the most significant benefits of the hybrid approach:
- Scalability: With a hybrid database system, your infrastructure can easily scale up, down, or out depending on your organization’s requirements. This provides flexibility in handling increased workloads, without the need to invest in additional hardware for on-premises databases.
- Cost-efficiency: Utilizing a hybrid solution lets you optimize costs by selecting the best-suited services for each database need. For instance, you can save on operational costs by moving non-critical data to the cloud while maintaining critical, sensitive data on your on-premises servers.
- Security and Compliance: Hybrid databases give your organization the choice to store sensitive data on-premises, ensuring adherence to regulatory requirements and data protection standards. This enables businesses to take advantage of the cloud’s flexibility, while still maintaining necessary security precautions.
- Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity: A hybrid approach brings more resilience to your data ecosystem, with data being stored and backed up on-premises and in the cloud. This ensures business continuity in case of local outages or disasters.
Example: ACME Corporation, a global manufacturing company, opted for a hybrid database solution to manage its growing data demands. This allowed them to leverage the speed and scalability of cloud databases for customer-facing applications and the security of on-premises databases for their sensitive financial and manufacturing data.
Conclusion
Selecting the right database solution for your business largely depends on your organization’s unique needs and objectives. Cloud databases offer the benefits of scalability, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness, while on-premises databases provide greater control, customization, and security for certain sensitive data types.
A hybrid approach combines the strengths of both, allowing for flexibility and adaptability. When deciding between cloud, on-premises, or hybrid databases, consider factors such as size, scalability, cost, and specific data requirements.
By taking the time to thoroughly analyze the benefits and drawbacks of each option, developers and business owners can make an informed decision that best suits their data storage and management needs. Ultimately, the right choice will depend on the specific use case and the desired balance between the advantages of each option.
Ready to innovate and transform your business? Say hello to CodeBeavers!
If you are looking for ways to bring your product or app ideas to life? We’ve got your back. CodeBeavers has the tools and engineers you need to make your projects come alive. With CodeBeavers, you’ll be able to build faster than ever, deploy code with ease, and scale like never before. Send us your requirements now, and let’s start winning together.